Configure Components
Create and Configure Secret for MySQL Database
In this step, you create a Kubernetes secret component for the MySQL database. This is necessary because the configuration below is in the environment variables section of the mysql-deployment YAML file.
env:
- name: MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: mysql-pass
key: password
Before you proceed, choose a password and convert it into base64 format. You can use an online tool for this conversion. For this example, the password is password and its base64 encoding is cGFzc3dvcmQ=.
- Click on the Kubernetes icon on the dock, search for
secret, and click on it or drag it to the canvas.

Figure: Create secret component
Click on the Secret component to open the configuration window.
- Set the name as
mysql-pass - Set the Type as
Opaque - Click + next to Data and add the secret as a key-value pair
password:cGFzc3dvcmQ=
- Set the name as
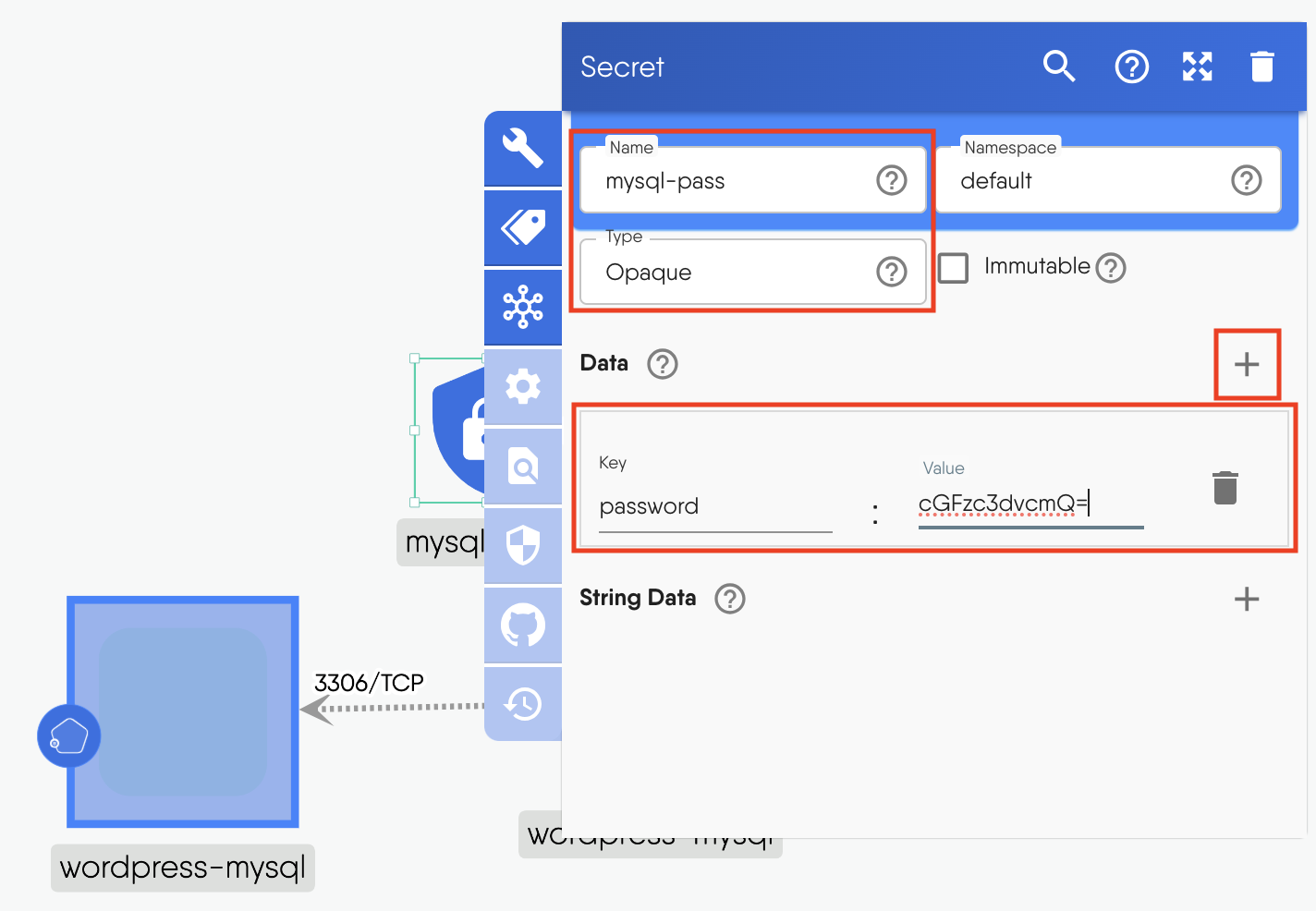
Figure: Configure secret
- Click outside the window to close the configuration tab.
Create Persistent Volumes
MySQL and WordPress each require a Persistent Volume (PV) to store their data.
For this tutorial, you will use the manual StorageClassName and set the Persistent Volume to use the hostPath type.
Please note that using hostPath for Persistent Volumes is generally not recommended for production environments because it ties the volume to the node’s filesystem, which can lead to data loss if the node fails. However, you can use it in this tutorial for development purposes.
- Click on the Kubernetes icon on the dock, search for
Persistent Volume, and select it. Create two PVs.
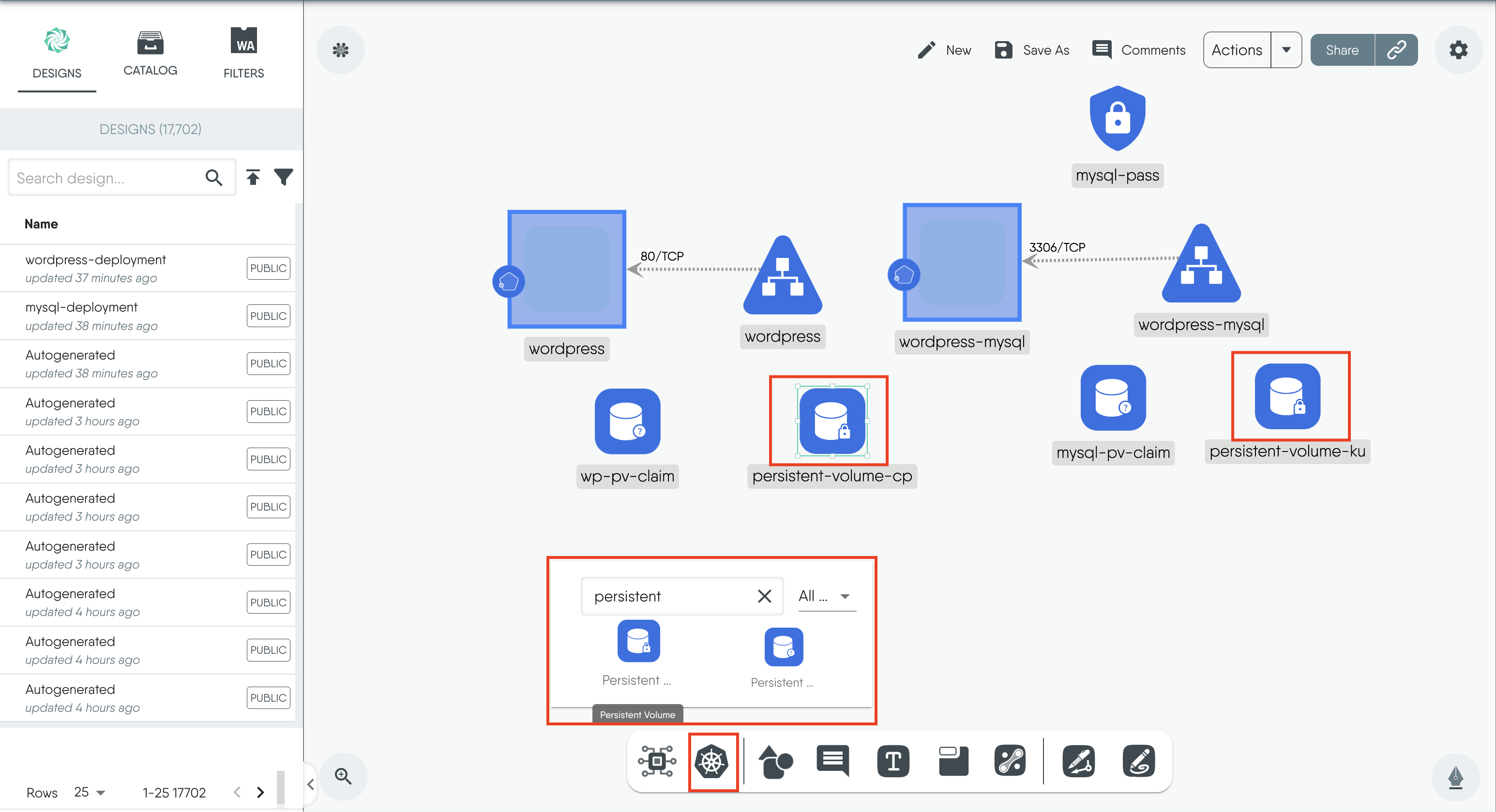
Figure: Create persistent volume
Click on the wordpress PV to open the configuration window.
- Change the “name” to
wp-pv - Set the “StorageClassName” as
manual - Click + next to “AccessMode” and enter
ReadWriteOnce
- Change the “name” to
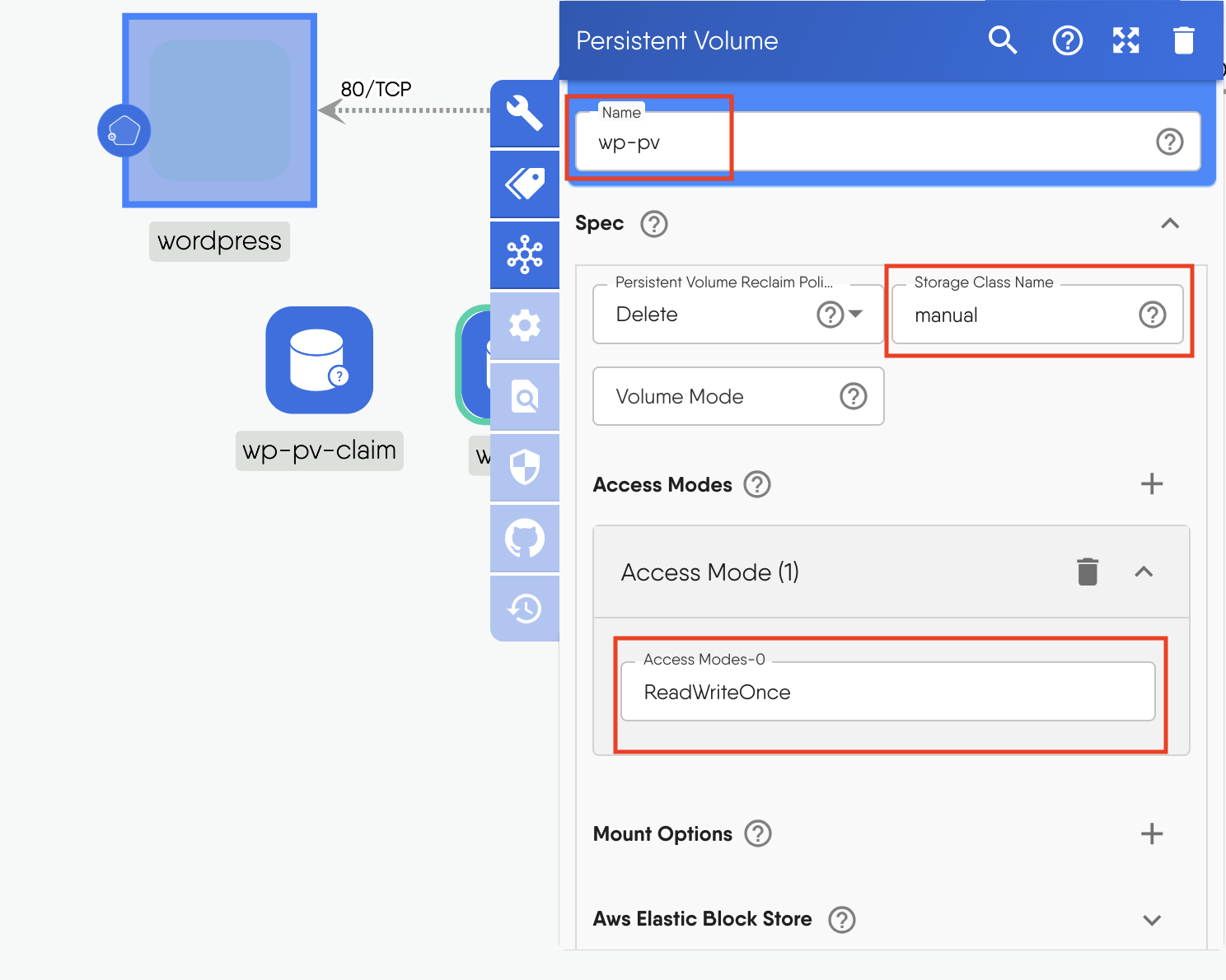
Figure: Configure persistent volume
- Scroll down to "Capacity" and enter the key pair `storage:20Gi`
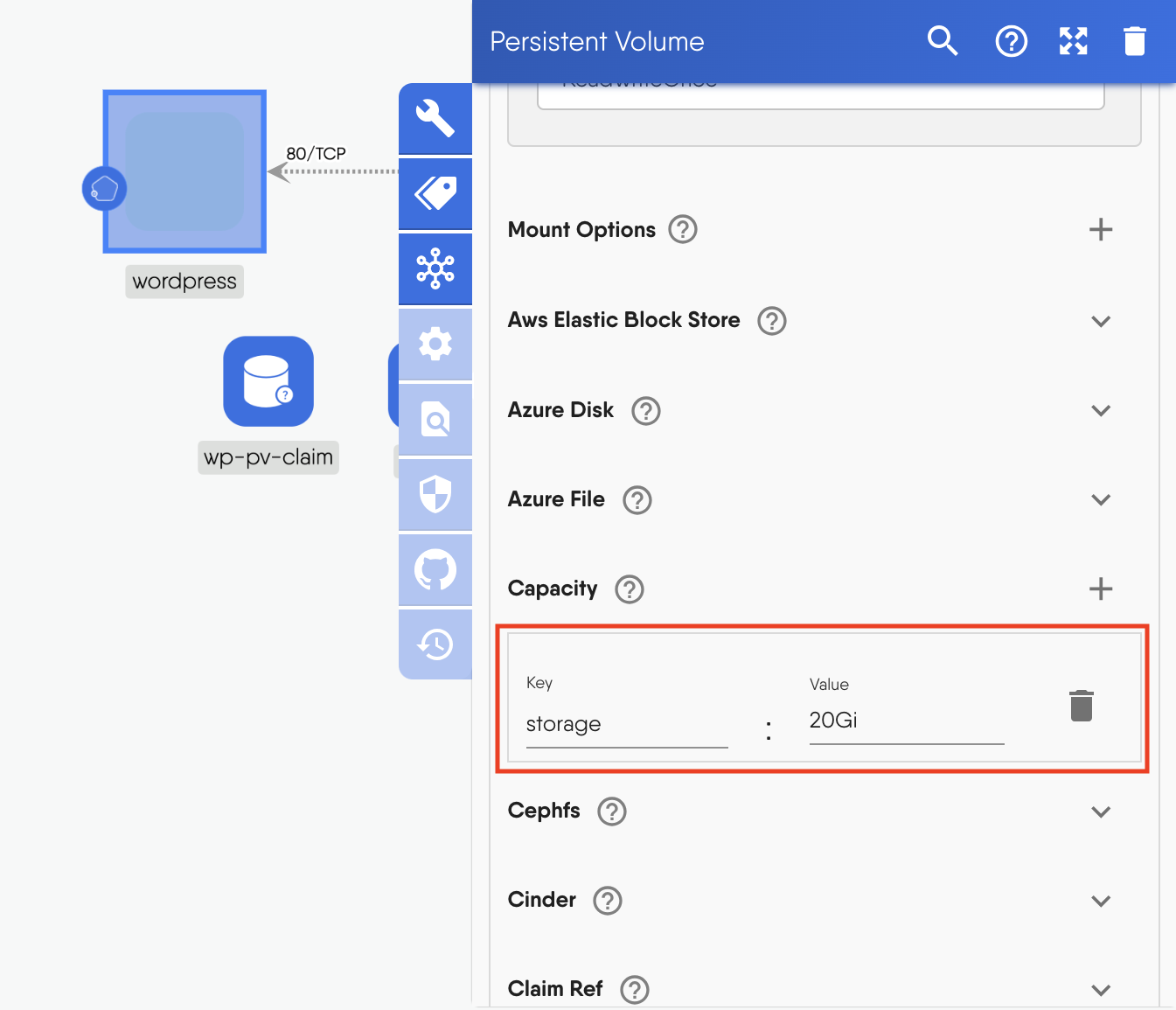
Figure: Persistent volume capacity
- Scroll down to "Hostpath" and input `mnt/data/wp-pv` for the _path_ and `DirectoryOrCreate` for the _type_.
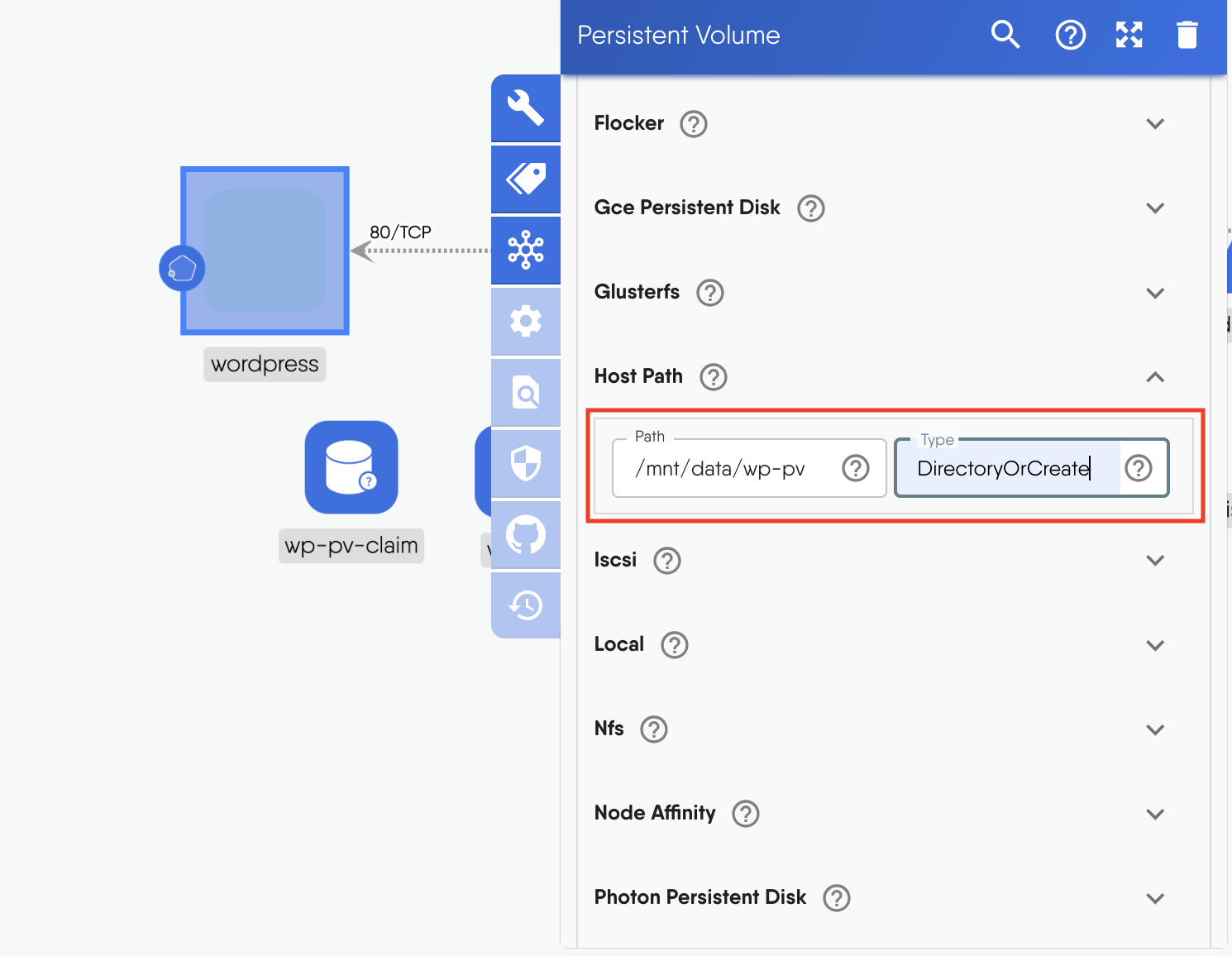
Figure: Persistent volume hostpath
Repeat similar steps for the MySQL Persistent Volume
- Click on the MySQL PV to open the configuration window.
- Change the “name” to
mysql-pv - Set the “StorageClassName” to
manual - Click + next to “AccessMode” and set it to
ReadWriteOnce - Scroll down to “Capacity” and enter the key pair
storage:20Gi - Scroll down to “Hostpath” and input
mnt/data/mysql-pvfor the path andDirectoryOrCreatefor the type.
Click on
wp-pv-claimandmysql-pv-claimand set their “StorageClassName” asmanual.